What Is the Mobile Concrete Batching Plant?
Understanding the Mobile Concrete Batching Plant
A mobile concrete plant, also known as a portable concrete batching plant, is a facility that combines various ingredients to create concrete. These ingredients typically include water, air, cement, aggregates (such as sand, gravel, or crushed stone), and admixtures (chemicals that alter the properties of the concrete). Unlike stationary plants, mobile concrete plants are designed for easy transportation, offering flexibility and efficiency for construction projects.
Mobile concrete batching plants are specialized equipment used for mixing and batching concrete on-site. They can be quickly assembled and disassembled, making them ideal for different project sites. In the dynamic construction world, efficiency and mobility are crucial.
Production Capacity
The production capacity of a mobile concrete plant refers to the amount of concrete it can produce within a specified time frame, typically measured in cubic meters per hour (m³/hr). For instance, a plant with a capacity of 100 m³/hr can produce 100 cubic meters of concrete every hour, ensuring a steady and reliable supply for large-scale projects. This output level is ideal for infrastructure projects, commercial developments, and residential buildings, helping to reduce downtime and accelerate construction timelines.
Types of Mobile Concrete Plants
Dry Mix Mobile Plant: In this type, all ingredients except water are mixed together in a dry form, with water added separately during transportation or directly at the site.
Wet Mix Mobile Plant: Here, all ingredients, including water, are mixed together in the plant, providing a more homogeneous mix that is suitable for high-quality concrete production.
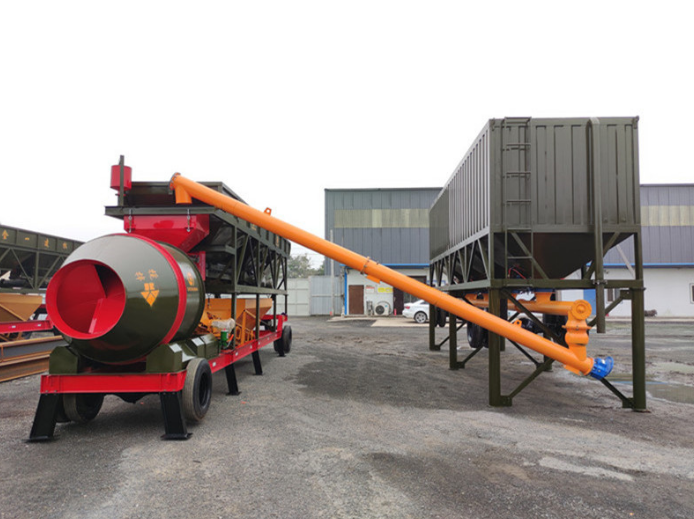
Main Structure of Mobile Concrete Batching Plant
Mobile concrete batching plants typically consist of several components that share similarities with stationary concrete batching plants, including:
- Aggregate Bins: These are storage bins for different sizes of aggregates (such as sand, gravel, and crushed stone) used in concrete production. For example, a 60 m³ mobile concrete plant has four 9 m³ aggregate hoppers, totaling 36 m³ capacity, allowing for the use of four different aggregates. We provide extensive solutions for various types and capacities of aggregate hoppers—contact us for more information.
- Conveyor Belts: Conveyor belts transfer aggregates from storage bins to the mixer. Longer conveyor belts require more powerful electric motors and specific configurations to ensure movement; otherwise, the motors may not operate efficiently over extended periods. Two types of conveyor belts are used in mobile concrete plants: one for weighing aggregates and the other for transferring them to the mortar mixer.
- Cement Silo: This is a storage container for cement powder, which serves as a binder in concrete production.
- Mixer: The heart of the batching plant, where aggregates, cement, water, and other additives are mixed to produce concrete. Twin-shaft mixers are commonly used in these mobile plants to achieve a more homogeneous concrete mixture.
- Control System: An integrated control system monitors and regulates the batching process, including mixing time, water content, and other parameters.
Advantages of Mobile Concrete Plants
Mobile concrete batching plants offer several advantages, including flexibility, mobility, and cost-effectiveness. They are especially useful for construction projects that require on-site concrete production, such as road construction, building foundations, and infrastructure projects in remote locations.
While mobile concrete batching plants have many benefits, there are also some disadvantages to consider:
- Limited Production Capacity: Mobile concrete plants typically have smaller production capacities compared to stationary counterparts. This limitation may not be suitable for large-scale construction projects that require high volumes of concrete.
- Higher Initial Investment: The initial cost of acquiring a mobile concrete batching plant, especially one with advanced features and mobility options, can be higher than that of stationary plants. This investment may deter some construction companies with budget constraints; however, it becomes more sensible for long-term use, akin to stationary concrete plants.
- Dependency on Transportation: Mobile batching plants rely on transportation to move between project sites. This dependency on trucks or trailers can introduce logistical challenges, particularly in areas with limited access or rough terrain.
- Setup and Dismantling Time: Although mobile plants are designed for easy setup and dismantling, this process still requires time and labor. Construction teams need to allocate resources for assembling the plant at each new site, which can affect project schedules and timelines.
- Less Stability and Durability: Mobile concrete plants may have less stability and durability compared to stationary plants due to their portable nature. Frequent movement, exposure to harsh weather conditions, and rough handling during transportation can contribute to wear and tear over time.
- Space Limitations: Mobile batching plants require adequate space for setup and operation. In congested or confined construction sites, finding suitable space for deploying the plant can be challenging and may limit its effectiveness.
- Potential Maintenance Issues: The mobility and portability of mobile concrete plants can complicate maintenance and servicing. Components such as wheels, axles, and towing mechanisms may require regular inspection and upkeep to ensure optimal performance.
- Environmental Impact: While mobile plants offer environmental benefits, such as reduced transportation emissions, their operation still contributes to noise pollution and disturbances at construction sites. Proper planning and mitigation measures are necessary to minimize the environmental impact of mobile batching plants.
Despite these disadvantages, mobile concrete batching plants remain valuable assets for construction projects that require on-site concrete production and flexibility. By carefully assessing project requirements and weighing the pros and cons, construction companies can determine whether a mobile plant is the right fit for their needs.
How to Move the Mobile Batching Plants?
Mobile concrete batching plants are designed for easy transportation between different project sites, and there are several ways these plants can be moved:
- Towable Trailer: Many mobile concrete batching plants are mounted on trailers with wheels, allowing them to be towed by a truck or other suitable vehicle. This design facilitates transportation on roads and highways to various project locations. Once on-site, the trailer can be stabilized and leveled for operation.
- On-Site Mobility: Some mobile batching plants come equipped with built-in axles and wheels, enabling them to be moved around the site using a towing vehicle or manually pushed and pulled. This on-site mobility provides flexibility in positioning the plant closer to the construction area or optimizing space utilization.
- Containerized Design: Certain mobile concrete batching plants are containerized, housed within standard shipping containers. These plants can be transported via truck, rail, or ship to different locations, offering greater mobility and versatility for international or remote projects.
- Modular Construction: Modular mobile batching plants consist of prefabricated modules that can be easily transported and assembled at the desired site. This construction method allows for quick setup and dismantling, making it ideal for temporary or mobile construction projects.
What Should Be Considered While Purchasing a Mobile Concrete Batching Plant?
These considerations are also mentioned in our previous blog, which I highly recommend you read regarding stationary concrete plants.
- Production Capacity: Determine the required production capacity of the plant based on your project’s needs.
- Mobility and Transportability: Evaluate the plant’s mobility features, including ease of transportation, setup, and dismantling. Consider factors such as size, weight, and available towing options.
- Quality of Components: Assess the quality and durability of the plant’s components, including the mixer, conveyor belts, aggregate bins, and control system. Opt for reputable brands known for reliability and longevity.
- Mixing Performance: Consider the mixing performance and efficiency of the plant, including mixing time, homogeneity of the concrete mix, and the ability to handle different types of aggregates and admixtures.
- Batching Accuracy: Check the accuracy of the batching system in proportioning aggregates, cement, water, and additives. Accurate batching is crucial for producing high-quality concrete with consistent properties.
- Environmental Considerations: Evaluate the environmental impact of the plant, including noise levels, emissions, and dust control measures. Choose a plant that complies with local environmental regulations.
- Maintenance and Support: Consider the availability of spare parts, technical support, and after-sales service from the manufacturer or supplier. A reliable support network is essential for minimizing downtime and ensuring smooth operation.
- Cost and Budget: Compare the initial purchase cost, installation expenses, and ongoing operational costs of different plant options. Balance upfront investment with long-term value and performance.
- Customization Options: Determine if the plant can be customized to meet specific project requirements or if additional features and accessories are available.
- User-Friendly Design: Look for a plant with a user-friendly design and intuitive control interface to simplify operation and maintenance tasks.