How an Asphalt Plant Works?
Asphalt, a commonly used material in road construction, is produced in specialized facilities known as asphalt plants. These plants are responsible for the production of hot mix asphalt (HMA), which is a blend of aggregates, binder (usually asphalt cement), and sometimes additives. The process of producing asphalt involves several stages and components working together to ensure the proper heating, mixing, and storage of the materials. In this article, we will explore how an asphalt plant works, highlighting the key processes and components involved.
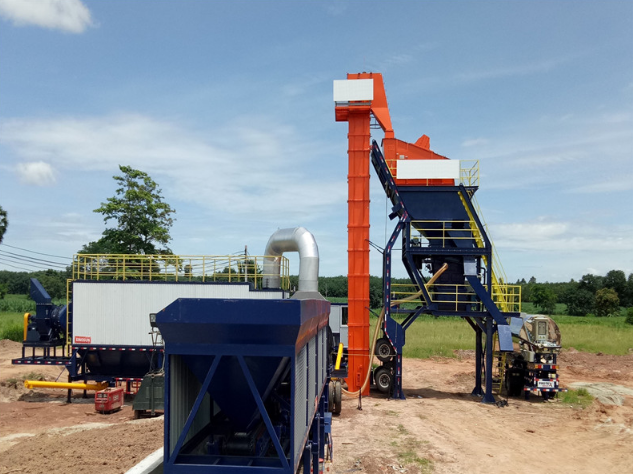
Compulsory type mobile asphalt plant
1. Aggregate Handling and Storage:
The production of asphalt begins with the handling and storage of aggregates, which are the granular materials used as a base for asphalt. Aggregates, such as crushed stone, sand, or gravel, are stored in separate bins or silos at the asphalt plant. Each type of aggregate is stored in a specific bin to ensure the proper blending of materials during the mixing process. The aggregates are typically stored in a heated environment to prevent moisture accumulation and maintain their desired temperature.
2. Drying and Heating of Aggregates:
Before the mixing process can take place, the aggregates need to be dried and heated to remove any moisture and reach the optimal temperature for mixing with the asphalt binder. The aggregates are transported from the storage bins to a dryer drum or a rotating kiln-like chamber within the asphalt plant. Inside the drum, hot air is blown through the aggregates, effectively drying and heating them. The heated aggregates exit the dryer drum and are conveyed to the next stage of the process.
3. Mixing of Aggregates and Binder:
Once the aggregates have been properly heated and dried, they are mixed with the asphalt binder. The binder, which is typically asphalt cement, is stored in heated tanks at the asphalt plant. The binder is pumped from the storage tanks and introduced into the mixer, where it combines with the aggregates. The mixing process ensures a thorough and uniform distribution of the binder, coating each aggregate particle. The mixing time and temperature are carefully controlled to achieve the desired consistency and workability of the asphalt mix.
4. Addition of Additives (Optional):
In some cases, additives may be introduced into the asphalt mix to enhance specific properties or address certain requirements. Additives can include modifiers, polymers, or rejuvenators, depending on the desired characteristics of the final asphalt mix. These additives are typically stored in separate tanks and metered into the mixer at the appropriate stage of the mixing process. The addition of additives requires precise control to ensure the proper dosage and distribution throughout the asphalt mix.
5. Storage and Loadout:
Once the asphalt mix has been thoroughly mixed and blended, it is transferred to storage silos or hot bins. These storage facilities allow for the temporary storage of the hot mix asphalt until it is ready for loadout and transportation to the construction site. The storage silos are equipped with temperature controls to maintain the heat of the asphalt mix. When the mix is ready to be loaded onto trucks, it is discharged from the storage silos or hot bins and transported to the designated loading area.
6. Emission Control and Environmental Considerations:
Asphalt plants generate various emissions during the production process, including particulate matter, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and potentially odorous fumes. To minimize the environmental impact, asphalt plants employ several measures for emission control. These may include the use of baghouses or filters to capture particulate matter, the installation of scrubbers or cyclones to remove pollutants from exhaust gases, and the use of odor control systems to mitigate any unpleasant odors. Asphalt plants also comply with local regulations and standards regarding emissions and environmental protection.
Conclusion
An asphalt plant is a complex facility that combines various processes and components to produce hot mix asphalt. From aggregate handling and storage to drying and heating, mixing with the binder, potential addition of additives, storage, and loadout, each stage is carefully orchestrated to ensure the proper production of asphalt. Emission control and adherence to environmental regulations are integral parts of the asphalt plant operation. Understanding how an asphalt plant works helps to appreciate the complexity involved in producing the essential material used in road construction.